Key Takeaways:
- Sustainable finance is essential for emerging markets, balancing economic growth with environmental and social responsibility.
- Regulatory inconsistencies, limited capital access, and low ESG awareness hinder its adoption.
- Growing demand for green investments, fintech innovations, and international funding creates expansion opportunities.
- China's success in green bonds and India's renewable energy financing highlight the impact of strong policies and investments.
- Strengthening policies, ESG education, and technology-driven solutions can accelerate sustainable finance in emerging markets.
The global financial landscape is undergoing a significant transformation as the emphasis on sustainability grows. Sustainable finance, which integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial decision-making, is becoming increasingly vital. In particular, sustainable finance has become a crucial aspect of global financial markets, especially as the world grapples with climate change and environmental degradation. Emerging markets, characterized by rapid economic growth and industrialization, face unique challenges and opportunities in promoting finance. As a result, several unique challenges and opportunities for promoting sustainable finance in emerging markets have emerged, including the need for innovative financial instruments, capacity building, and regulatory frameworks that align with local development goals and global sustainability standards.
The Landscape of Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are nations with rapidly growing economies and increasing integration into the global economy. These markets, including countries like Russia, India, China, and South Africa (BRICS), are characterized by high economic growth rates, substantial foreign investment, and significant industrialization. However, they often face volatility and economic instability due to political, social, and environmental factors.
Emerging markets are in a paradoxical situation where rapid economic growth and industrialization lead to environmental degradation and resource depletion. This context creates a critical need for sustainable finance mechanisms that can balance economic development with environmental conservation. Sustainable finance in these regions can address climate change and promote long-term economic stability.
Challenges of Promoting Sustainable Finance in Emerging Markets
The main obstacle to sustainable finance development stems from inconsistent regulatory frameworks and inadequate supportive policies . Emerging markets face difficulties as they have insufficient regulations which promote green investments through incentives or mandate ESG disclosure reporting. The diverse nature of regulations between different countries creates additional obstacles to sustainable finance promotion. Secondly, obtaining affordable capital presents a significant obstacle to sustainable projects. Emerging market financial institutions tend to avoid risks by funding established industries instead of supporting innovative sustainable projects. This risk aversion of financial institutions restricts capital from reaching sustainable development projects. Thirdly, another barrier is the lack of awareness and understanding of sustainable finance among shareholders. Emerging market financial institutions, together with businesses and investors, face difficulties in implementing ESG criteria as they lack sufficient expertise and knowledge about sustainable decision-making. The development of educational programs stands as a fundamental requirement to address this issue. Finally, underdeveloped financial market infrastructure represents a fundamental obstacle to progress. Emerging markets face challenges because they require financial products and services which support sustainable finance. The lack of green financial instruments, including green bonds and sustainability-linked loans, prevents investors from directing funds toward sustainable projects.
Opportunities and Strategies for Scaling Sustainable Finance in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets experience continuous growth in green investment demand despite current market barriers. The rising importance of sustainability among consumers and investors enables financial institutions to create and introduce green financial products. The International Finance Corporation (IFC) predicts that emerging markets will receive 24 trillion dollars for green building investments by 2030 thus accelerating sustainable development and economic growth. The sustainable financial instruments market shows strong potential for expansion. Moreover, the advancement of technology, together with innovation, serves as fundamental catalysts for sustainable finance development. Financial technology (fintech) systems enhance capital accessibility while making financial markets operate more efficiently and transparently. The blockchain system enables secure and transparent green project transactions and artificial intelligence systems help organizations evaluate and control ESG risks.
Furthermore, international organizations and development banks are fundamental in advancing sustainable finance throughout emerging markets. The World Bank, together with its subsidiary IFC, supports emerging markets by offering funding, technical expertise and capacity development programs. The 2023 World Bank impact report demonstrated that 690 projects received funding of over 38 billion dollars to support sustainable development and growth. The combination of successful partnerships with funding programs serves as a catalyst for sustainable finance projects in developing nations. Finally, the emerging market's sustainability policies have recently shown positive developments. Governments now establish forward-thinking policies and regulatory systems which back sustainable finance initiatives. Green investment incentives, together with mandatory ESG reporting and green finance standard establishment, represent recent developments in sustainable finance.
Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Finance Initiatives
Case Study 1: Green Bonds in China
Green bonds function as powerful financial tools which help emerging market economies fund sustainable project development. The Chinese green bond market advanced through government support, clear regulatory systems and robust investor demand, enabling the funding of multiple sustainable projects. Chinese green bond issuance volume has shown significant growth from 2019 to 2023, with total investments increasing from $59.26 billion in 2019 to a peak of $131.37 billion in 2022. However, the market experienced volatility, with a notable 26.46% decline in 2020 and a 16.02% decrease in 2023 after the 2022 peak. The most substantial growth occurred between 2020 and 2021, with an 87.82% increase, reflecting strong recovery and significant interest in green investments. China's success with green bonds demonstrates the potential of this financial instrument to mobilize large-scale investments in sustainability.
Figure 1: Green Bond Yearly Investment and Percentage Increase Issuance in China from 2019 to 2023
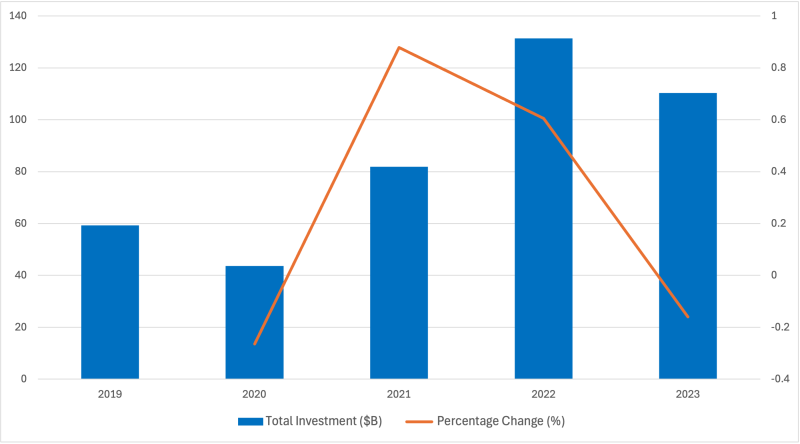
Source: Ramos and Wu (2024)
Figure 2: Internationally (Non)aligned Green Bond Issuance in China from 2019 to 2023
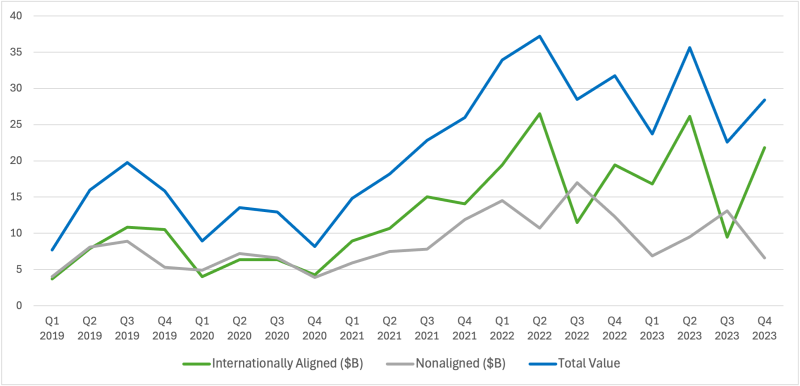
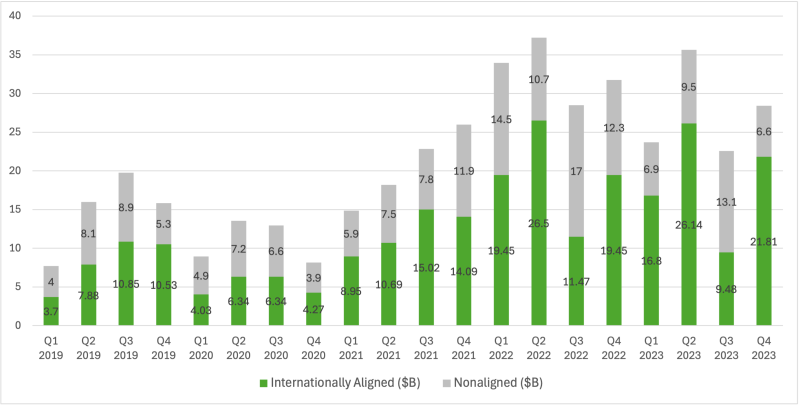
Source: Ramos and Wu (2024)
Case Study 2: Renewable Energy Financing in India
The Indian renewable energy sector rapidly expanded because of new financing approaches. The government has created policies which aim to draw both domestic and international investors into renewable energy projects. These successful initiatives prove that specific policy measures combined with international backing can drive sustainable finance. In particular, India has made significant strides in expanding its renewable energy capacity. Between 2021 and 2023, the country saw substantial growth in both solar and wind energy installations. India's total renewable energy capacity expanded from 85,270 MW in 2021 to 114,358 MW in 2023, highlighting its strong commitment to expanding its renewable energy infrastructure. This growth reflects the success of India's policies and investments in promoting renewable energy.
Figure 3: Total Renewable Energy Capacity in India from 2021 to 2023
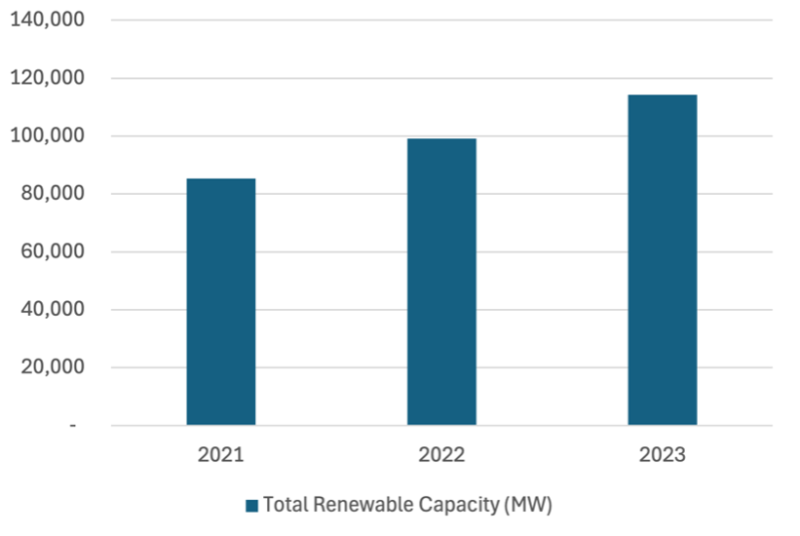
Source: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India (2024)
Figure 4: Breakdown of Total Renewable Energy Capacity in India by Source from 2021 to 2023

Source: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India (2024)
Strategies for Scaling Sustainable Finance in Emerging Markets
The development of supportive policies , together with regulatory frameworks, represents an essential requirement for the expansion of sustainable finance. Governments need to create financial incentives for green investments while requiring ESG disclosure reporting and forming clear guidelines for sustainable finance. The implementation of consistent regulatory standards and coordinated policies by policymakers will enable cross-border sustainable investments. Moreover, sustainable finance requires the development of comprehensive financial ecosystems which support its growth. This requires the expansion of financial institutions' capacity, as well as green financial product development and stakeholder collaboration promotion. Financial institutions should be encouraged to include ESG criteria in their lending and investment practices.
Furthermore, the implementation of targeted education and training programs must be established to boost understanding and awareness of sustainable finance among stakeholders. All financial professionals, together with businesses and investors, need to develop capabilities for ESG risk evaluation and management. Capacity-building programs help create local sustainable finance experts who drive new innovations in this field. Finally, the implementation of technology and innovative solutions will boost sustainable finance operations in emerging markets. Digital lending platforms, together with mobile banking services through fintech solutions, enhance both financial service accessibility and capital availability. The implementation of blockchain technology and artificial intelligence systems enables sustainable finance operations to become more transparent while achieving higher efficiency and better risk management capabilities.
Conclusion
Sustainable finance within emerging markets faces both obstacles and potential benefits. The path to progress faces obstacles from regulatory barriers, limited capital access and low awareness yet rising green investment demand, technological advancements and global support systems create potential solutions. Emerging markets require robust financial systems alongside strong regulatory frameworks and investments in education and technology to achieve large-scale success. Sustainable finance adoption creates economic growth together with environmental conservation and social well-being which leads to global sustainability and climate action.
Link 1 ; Link 2 ; Link 3 ; Link 4 ; Link 5 ; Link 6 ; Link 7 ; Link 8 ; Link 9 ; Link 10 ; Link 11